Supply Chain Management 101: Principles, Examples, and Templates
Globalization has become an undeniable part of commerce over the last few decades, as large companies have grown first to source labor and parts from developing regions, and then to start selling in those same areas as they grew in wealth and buying power. Supply chains have had to keep in step, passing through numerous countries to obtain goods most efficiently and cost effectively, and growing more complex as a result. And on the other end, the supply chain grows more frayed in order to deliver to countless countries for consumption. For the largest companies, managing a supply chain can require dedicated teams in every area the chain touches. It’s safe to say that supply chain management is both an art and a science.
This article will cover what a supply chain is, with examples; discuss how supply chain management works and its principles; and vital concepts in the field. Then we’ll move on to current issues and where the field is going. Finally, you’ll find useful resources, templates, and education programs. Ready? Let’s get started.
What Is a Supply Chain?
A supply chain is a collection of suppliers required to create one specific product for a company. The chain is made up of nodes or “links,” which can include multiple manufacturers for parts, then the completed product, then the warehouse where it is stored, then its distribution centers, and finally, the store where a consumer can purchase it. The concept of the chain is important, because each link is connected in a specific direction and order, and the next link cannot be reached without going through the previous one. Each link adds time and costs, and can involve labor, parts, and transportation. Every product a company carries may have its own supply chain, though they may use certain suppliers for multiple products. You can see why this gets so complicated, especially for international supply chains.
The process described above was that of a typical retail supply chain. However, there are many different types in practice. Here are three examples from well-known masters of supply chains:
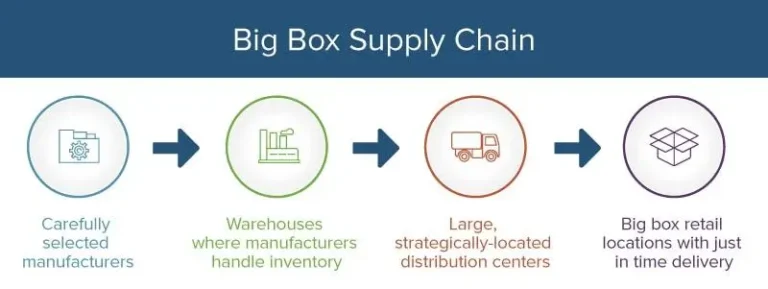
Example: Walmart and “Big Box” Retailers
The rise of the “Big Box” store, epitomized by Walmart, has profoundly reshaped the retail landscape with its emphasis on size, widespread presence, and meticulously planned supply chains aimed at outpacing competitors. A critical question arises: how does a company like Walmart turn a profit on a $5.00 t-shirt manufactured overseas?
Walmart’s success can be attributed to several strategic supply chain practices. Firstly, the company minimizes supply chain links by sourcing generic goods directly from manufacturers, bypassing suppliers with brand names and associated markups. This direct approach allows Walmart to negotiate lower prices and maintain control over inventory.
One key strategy employed by Walmart is “Vendor Managed Inventory” (VMI), wherein manufacturers are tasked with managing products within Walmart’s warehouses. This arrangement streamlines operations, reduces inventory holding costs, and ensures efficient product availability.
Moreover, Walmart is highly selective in its choice of suppliers. It partners only with those capable of meeting its high-volume demands at competitive prices. Location plays a crucial role as well, with Walmart strategically choosing suppliers located close to distribution centers to minimize transportation costs and improve supply chain efficiency.
Additionally, Walmart operates its supply chain as an integrated entity, fostering collaboration and communication among all partners on a unified network. This cohesive approach enhances visibility, coordination, and responsiveness throughout the supply chain.
Furthermore, Walmart leverages economies of scale by purchasing goods in bulk quantities. This allows the company to negotiate favorable pricing terms with manufacturers and capitalize on cost efficiencies.
In terms of logistics, Walmart optimizes the movement of products directly from manufacturers to its warehouses and then to stores, which also function as distribution centers. This direct route reduces handling costs, inventory turnover time, and overall supply chain complexity.
Ultimately, Walmart’s strategic supply chain management enables it to offer products at competitive prices while maintaining profitability. By reducing supply chain links, leveraging economies of scale, and fostering efficient logistics, Walmart delivers value to consumers while remaining a dominant force in the retail industry.
Thank you for taking the time to read my blog! I hope you found it informative and engaging. Don’t forget to subscribe to stay up-to-date with our latest news and updates. Until next time, happy reading!
Motivation: We all need to learn from each other!
——————————————————————-
✳ Hey there, it’s Onkar Gill
🔺 A Supply Chain Expert!
✅ Let’s work together to take the procurement game to the next level!”
Like this post?
Want to see more stuff on Sourcing and Contracting?
🔔 Follow Onkar Gill
Connect with me
#procurement #sourcingandprocurement
#vendormanagement #procuretopay








Leave feedback about this